

Indicators for Clinics, Hospitals
Some KPIs grouped by type:
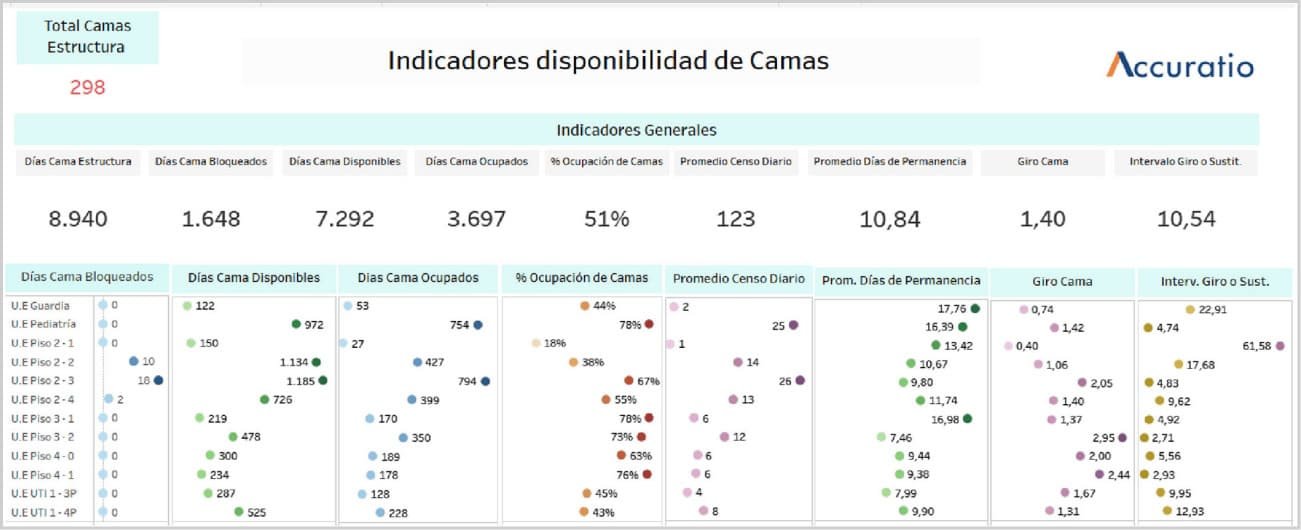
Indicators related to the availability of beds and the production of services.
The capacity of the inpatient sector of a Health Center that operates with this modality is measured by the number of beds available to care for patients who require hospitalization.
Average daily number of available beds
Average daily census
Bed occupancy rate
Bed turn
Turning or replacement interval
Average number of patients-days per discharge
Average number of days spent
Number of total expenditures and per operating unit
Number of total outpatient visits and per operating unit
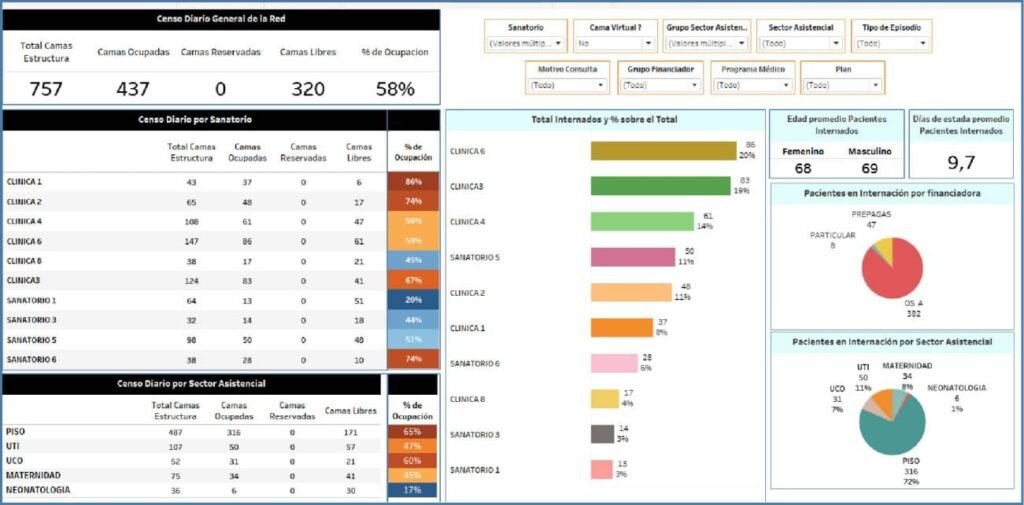
Indicators based on patient characteristics.
These indicators consider in their calculation formula the segmentation of the patient (age group, demographics, gender, level of education, employment status, others).
- Number of discharges according to selected variables that characterize the patient
- Number of outpatient medical consultations according to selected variables that characterize the patient
Indicators based on the care process or casuistry.
They are important for evaluating the care process. Indirectly, they are valid instruments for approaching the problem of quality of care. Based on the above, they are useful for monitoring the care process and help define priorities in decisionmaking, which is important when preparing the budget.
Number of discharges according to the main diagnosis at discharge by type of discharge and other variables indicative of the care process
In-hospital mortality rate Number of discharges according to main diagnosis at discharge by type of surgical and obstetric procedures
Number of outpatient medical visits according to diagnosis or reason for consultation
Percentage of mortality in surgical event
Number of hospital-acquired infections
Percentage of medication errors
Patient consultation time
Average length of stay in the emergency room
In the hospital setting, productivity indicators in operating theatres are essential to assess efficiency and optimise the provision of surgical services. Here are some of these indicators.
- Operating Room Utilization Time: Measures the percentage of time during which the operating room is being used for surgical procedures relative to the time available.
- Changeover time between procedures: Evaluate the time needed to prepare the operating room for the next procedure after one has concluded. A quick changeover reduces downtime and increases productivity.
- Resource utilization: Measures how resources, such as staff time, equipment, and supplies, are being used compared to needs and demand.
- Operating Room Occupancy Rate: Indicates how many of the available operating rooms are in use at any given time, which can help optimize scheduling and resource allocation.
- Surgery Cancellation Rate: Evaluates the percentage of scheduled surgeries that are canceled before they are performed. Cancellations can negatively impact efficiency and patient satisfaction.
- Surgical Infection Rate: Measures the incidence of surgical infections in patients undergoing surgery. It is crucial for evaluating and improving infection control protocols.
- Patient satisfaction: Assesses patients’ overall satisfaction with their surgical experience, including communication with staff, pain management, and post-operative care.
- Compliance with safety and sterilization protocols: Measures whether safety and sterilization protocols are being properly followed to prevent infection and ensure patient and staff safety.
- Readmission rate: Measures the percentage of patients who require to be readmitted to the hospital within a specific period after surgery. A high index may indicate quality problems in surgical care or postoperative follow-up.

Indicators related to the obstetric event.
Statistical information on reproductive (obstetric) events attended in health facilities is essential for health management. For each termination of a pregnancy, a minimum set of basic data is recorded that allows the mother’s data to be interrelated with those of the obstetric event in the same medium. As the data of the mother and the product of conception are interrelated, a complete record of the obstetric event can be kept, with the unit of analysis being the discharge due to an obstetric event.
Percentage of vaginal births
Percentage of caesarean sections
Percentage of live births according to low-birth-weight categories
Percentage of preterm live births
Percentage of post-secondary births
Percentage of fetal growth restriction
Percentage of large-for-gestational-age infants
Indicators of clinical effectiveness and health system outcomes.
They are important for evaluating the outcome of the care process or health care in healthcare facilities. Together with indicators based on the care process or casuistry, they are valid instruments to indirectly approach the problem of the quality of care and the results obtained as a result. Based on the above, they are useful for monitoring the results of care provided in health facilities in the inpatient modality and help to define priorities in decision-making, which is important when preparing
the budget.
Percentage of discharges according to selected categories of clinical effectiveness and health system outcomes
